Introduction of SAMA
Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority (SAMA) is the central bank of the kingdom of Saudi Arabia. It was established in 1952 as the kingdom's central money and banking authority. It regulates commercial, development, and other financial institutions in Saudi Arabia. It performs the following functions:
- Deals with banking affairs of the Government
- Issuing, regulating, and stabilizing the value of the national currency
- Managing foreign exchange reserves, monetary policies, etc
Introduction of SAMA Cyber Security Framework
SAMA Cyber Security Framework was established in May 2017 as a framework to fight against the cyber security risks for the financial institutes regulated by SAMA. The financial sector has menacing cyber threats and risk evolving, in this changing technology and business landscape. The SAMA Cyber Security Framework helps to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive information and online services. It protects sensitive information and online transactions from emerging threats in this rapidly growing technological world
The objective of the SAMA Cyber Security Framework
We have understood that the SAMA Cyber Security Framework helps in identifying and addressing the cyber security risk. The Framework was created based on the requirement of globally recognized cyber security standards such as NIST, PCI, ISO, BASEL, and ISF. Member organizations of SAMA and other financial institutions must adopt the SAMA Cyber Security Framework to achieve the following objectives:
- Create a common approach to deal with cyber security risks for the SAMA member organizations.
- Accomplish the appropriate level of maturity of the cyber security controls of the member organizations.
- Confirm that cyber security is risk-managed effectively within the SAMA member organizations.
Applicability of the Cyber Security Framework
The framework is mandated by SAMA. The SAMA is the owner and is responsible for periodically updating the Framework. The SAMA Cyber Security Framework is applicable to the following entities:
- Applies to all the banks operating in Saudi Arabia
- Applies to all the insurance companies operating in Saudi Arabia
- Applies to all financial service provider companies operating in Saudi Arabia
- Applies to all the bureaus operating in Saudi Arabia
- The financial market infrastructure
Overview of the Cyber Security Framework
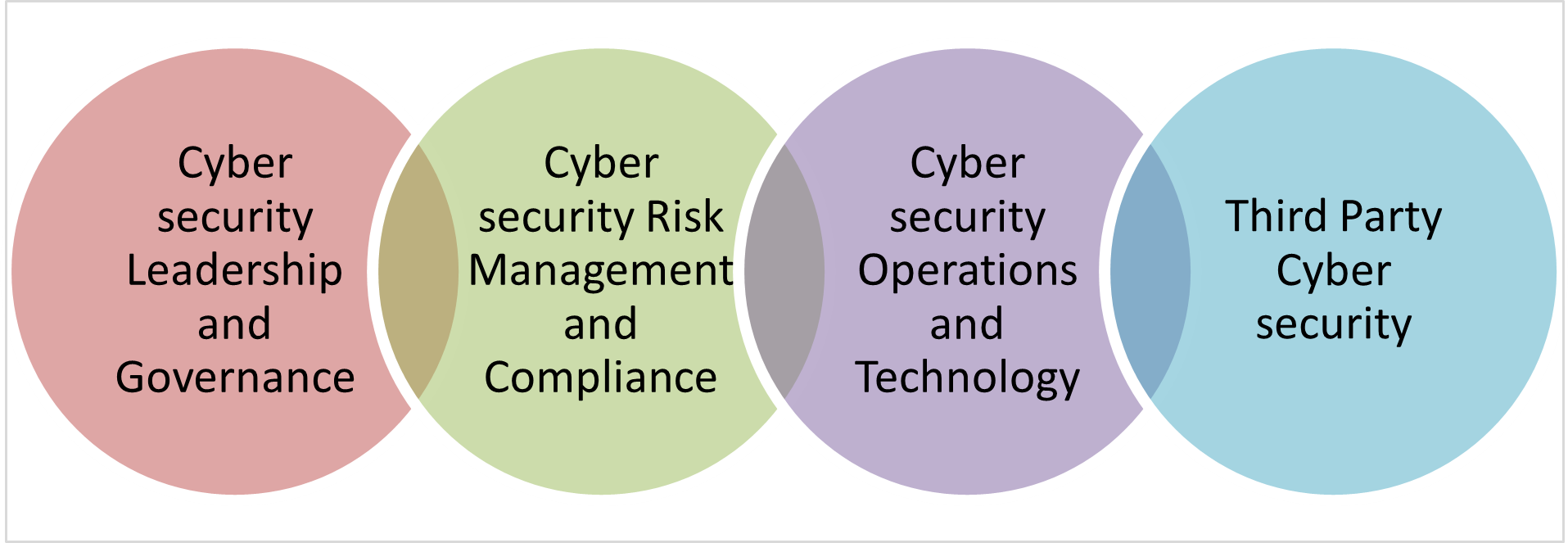
In the SAMA Cyber Security Framework there are mainly four domains that cover the following areas:
- Cyber Security Leadership and Governance
- Cyber Security Risk Management and Compliance
- Cyber Security Operations and Technology
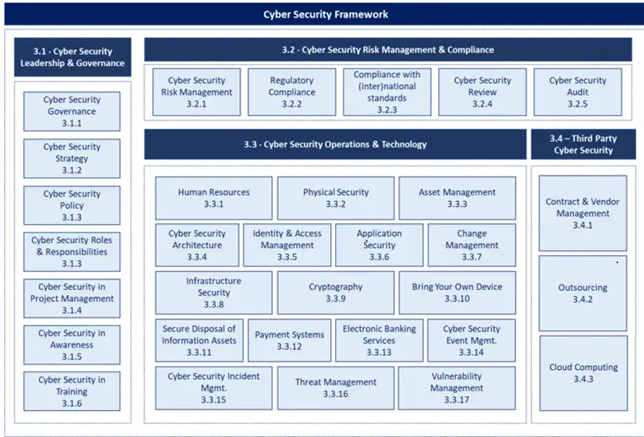
As we’ve discussed there are mainly four domains in SAMA Cyber Security Framework, also there are some sub-domains for each domain. A sub-domain focuses on a specific cyber-security topic. The below diagram shows the structure of the Framework and indicates the Cyber Security domains and sub-domains.
Maturity Models
In SAMA Cyber Security Framework, a predefined maturity model is established for the measurement of our organization's cyber security control environment. There are 6 maturity levels defined by the framework i.e. 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5. For achieving maturity levels, organizations have to meet the criteria of the levels of the maturity model. The maturity levels and the relevant criteria are summarized below:
Level 0- Non-existing
At this maturity level, the organization does not have any documentation about its processes and controls, and further, there is no awareness about the cyber security controls in the organization
Level 1- Ad-hod
At this level, no cyber security controls are defined and also the implementation of controls is inconsistent. The cyber security controls mitigate only identified risks and the execution of controls is inconsistent
Level 2- Repeatable but informal
At this level, the execution of cyber security is based on an informal and unwritten, though standardized practice. The cyber security control repetitions are present and the control objective and design are not formalized and approved
Level 3- Repeatable but informal
At this level, the controls are defined and approved formally; the implementation of controls can be demonstrated. The policies and procedures are well defined and documented. The key performance indicators are defined, monitored, and reported to evaluate the implementation
Level 4- Managed and Measurable
At this level, organizations assess the effectiveness of cyber security controls on a periodic basis and the same is documented
Level 5- Adaptive
At this level, the cyber security controls are subject to continuous improvement and cyber security controls are integrated with enterprise management framework and practices
Implementation Methodology
1. Planning
- Understanding the business and scope of implementation of SAMA Cyber Security Framework.
- Understanding the objective of an organization in terms of information security.
2. Gap Assessment
- Conducting Gap assessment against the requirements of SAMA Cyber Security Framework.
- Reviewing the existing documentation of the organization.
3. Risk Management
- Performing Risk Assessment for the organization based on the scope.
- Performing Risk Treatment.
4. Documentation
- Helping the organization in creating the supporting documents for SAMA compliance.
- Creating a security matrix for monitoring information security.
For more details, mail us at info@riskpro.in
